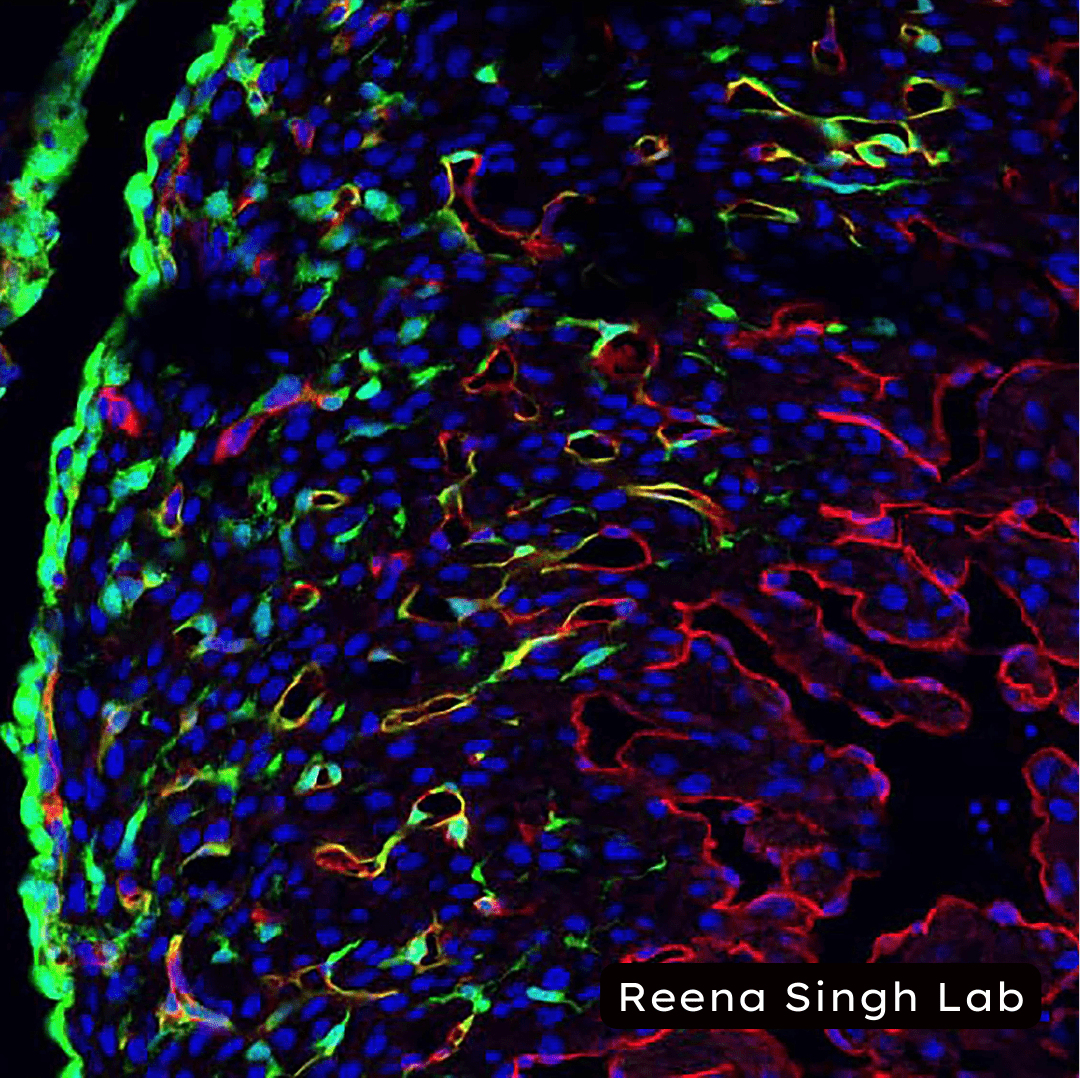
Future Potential : Impacts of Research
The pioneering research conducted in this lab holds the promise of transformative impacts across various domains, from medical sciences to healthcare and beyond. By harnessing the power of human pluripotent stem cell-derived 3D organoids and a multidisciplinary approach, the lab's work stands poised to catalyze significant advancements in understanding the underlying mechanism of disease, identify novel therapeutic targets, develop approaches for prevention and treatment for cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
Revolutionizing Disease Understanding:
The profound insights gained from studying 3D organoids could revolutionize our understanding of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes. Researchers will be better equipped to dissect the intricate molecular mechanisms underlying these complex disorders. This in-depth understanding could illuminate previously unidentified aspects of disease progression, enabling us to redefine disease classification and refine diagnostic criteria.
Precise Therapeutic Targeting:
As the lab unravels the molecular complexities of disease development, it will likely identify novel therapeutic targets previously unexplored. This knowledge could lead to the development of highly targeted drugs and therapies tailored to the specific genetic and molecular characteristics of individual patients. This personalized approach has the potential to enhance treatment efficacy while minimizing adverse effects.
Drug Discovery and Development:
The use of 3D organoids for drug screening and testing opens the door to accelerated drug discovery and development. By mimicking the physiological conditions more closely than traditional cell cultures or animal models, these organoids provide a realistic platform for evaluating potential drug candidates. This could drastically reduce the time and resources required for bringing new treatments to market.
Regenerative Medicine Breakthroughs:
The lab's exploration of vascular and pancreatic tissues and function through 3D organoids holds profound implications for regenerative medicine. The ability to generate functional cardiovascular and pancreatic cells from pluripotent stem cells could pave the way for innovative cell replacement therapies for diabetes and complications. This approach could potentially reverse disease symptoms and transform the landscape of diabetes management.
Enhancing Patient Care and Outcomes:
Ultimately, the lab's research has the potential to translate into tangible improvements in patient care and outcomes. From more accurate disease prediction to targeted interventions and regenerative treatments, individuals afflicted by cardiovascular diseases and diabetes could experience better quality of life and reduced disease burden.
Shaping Future Research Directions:
The nature of this research could also shape the trajectory of future scientific inquiries. As the lab uncovers new pathways, interactions, and cellular processes, it may inspire researchers across various fields to explore related areas, driving collaborative efforts and spurring further innovation.
Educational and Ethical Considerations:
The lab's work not only advances scientific knowledge but also raises important ethical and educational considerations. As society grapples with the implications of stem cell research, tissue engineering, and personalized medicine, this research could contribute to informed discussions and decisions about the ethical boundaries and societal implications of these emerging technologies.
In summation, the potential impacts of this lab's research are wide-ranging and transformative. By leveraging state-of-the-art techniques and interdisciplinary collaboration, the lab stands on the precipice of reshaping disease understanding, treatment paradigms, and the landscape of medical science itself.
Through its contributions to precision medicine, drug discovery, and regenerative therapies, this research holds the potential to significantly improve the lives of those affected by cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.Dr. Reena Singh
latest updates





Going through old files, found something from 2013. pic.twitter.com/RfRHSlJqTF
— Dr. Reena Singh (@ReenaSi05250192) March 28, 2021

